Orthopaedics 360 INFO
Hip Impingement can also be termed Femoroacetabular impingement. This is when there is a mismatch between the shape of the ball (femoral head) and the socket (acetabulum) in the hip. This can occur due to issues from a child, or can develop during an athletes sporting career. Femoroacetabular impingement can cause pain, particularly with squatting, lunging and kicking, and may result in early degeneration of the hip, and osteoarthritis. Until recent times, the surgical options for this condition involved major surgery, including dislocating the hip and cutting the bone. In current, arthroscopic methods, 95% of the pathologies to the hip can be addressed with keyhole surgery.
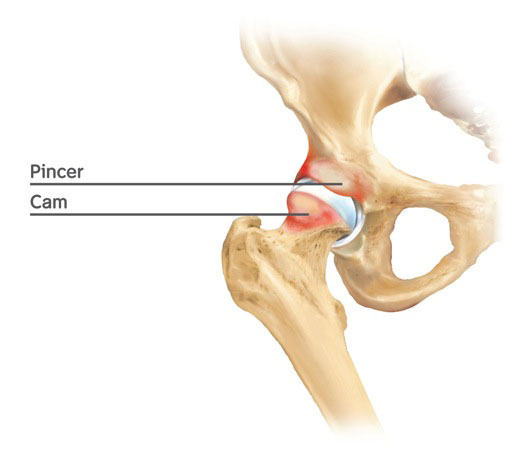
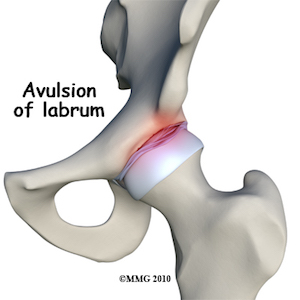
The image on the left shows the two main deformities in a hip resulting in restricted range of motion and groin pain. It may also result in a labral tear. The Labrum is a soft tissue structure that is attached to the edge of the acetabulum. Hip Impingement may cause:
- Joint Stiffness
- Pain when squatting, lunging, kicking a football
- Inflammation of the joint resulting in rest pain
- Lower back pain due to hip joint stiffness.
- A limp.
Once femoroacetabular impingement is found, investigations must be carried out to determine how bad the condition is, and what can be done. The initial first step is to have an Xray of the hip and pelvis, and then an MRI to view the soft tissue, cartilage, and to check the ligaments around the hip.
Non operative management options for femoroacetabular impingement are attempted first, after first determining if there are any major features in the hip that require surgery. If the deformity is mild, or the labral tear is small, then a period of rest, and an attempt at non operative management is warranted. This may include:
- Short course of anti-inflammatory medication (if approved by your general practitioner), to decrease associated inflammation around and within the hip joint.
- Glucosamine and Fish Oil – A large study performed in the USA found that there was a benefit in approximately 2/3rds of patients suffering from pain from inflammation of the knee or hip. This helped to reduce the perceived pain. Glucosamine and Fish oil act as a natural anti-inflammatory and can be a great supplement to your usual medications as the risks are comparatively low. Fish oil has other beneficial effects for the rest of the your body, not just your joints. These agents will never repair cartilage, but can act to prevent inflammation which can be harmful to a joint.
- A Local anaesthetic and steroid injection into the hip – this is often done as both a therapeutic and diagnostic method, and allows for a bit of an understanding as to what is happening in the hip, and the likely result from hip arthroscopic surgery.
- Weight loss – maintaining a healthy weight will decrease pain on any joint.
Operative Treatment
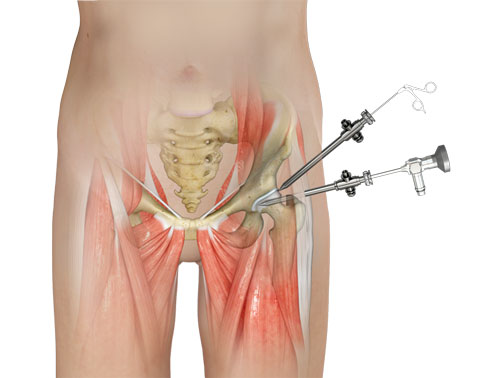
When non operative measures fail, the next step is to consider a hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopic hip surgery involves the use of a traction table, and specialised instruments to enable a surgeon to view most of the inside of the hip joint using small cameras and tools. Using small 1cm incisions around the hip joint, a Cam or Pincer lesion can be addressed, and a labral tear can either be derided (cleaned up) or repaired. A repair uses special anchors that are drilled into the bone that hold the labrum in place.
Being minimally invasive, a hip arthroscopy causes a lot less damage to the soft tissue to achieve the appropriate outcome. Using a series of specially made tools, advanced operations can now be performed with low risk.
Hip Labral Tears
Operative or non operative management
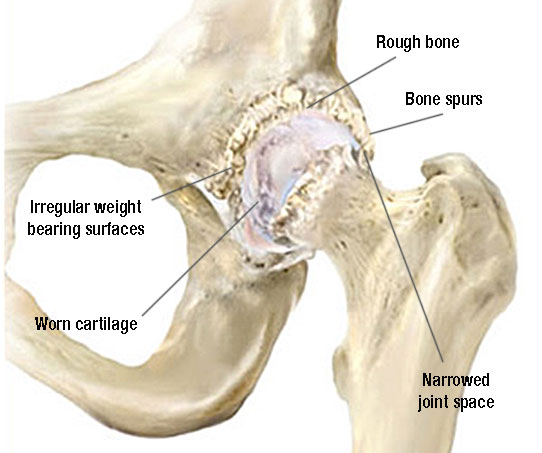
Hip Arthritis
Hip Arthritis should never debilitate quality of life.
Meniscus Tear
A guide to the humble meniscus tear and what you need to know
Orthopaedics 360
Orthopaedics 360
P: (08) 7099 0188
F: (08) 7099 0171
Southern Specialist Centre
Orthopaedics 360
P: (08) 7099 0188
F: (08) 7099 0171
Health @ Hindmarsh
Orthopaedics 360
P: (08) 7099 0188
F: (08) 7099 0171